概述
LRU(Least Recently Used),即最近最少使用算法,它的核心思想是当缓存满时,会优先淘汰那些近期最少使用的缓存对象。
该算法被应用在LruCache和DiskLruCache,分别用于实现内存缓存和磁盘缓存。
LruCache的介绍
LruCache是个泛型类,主要算法原理是把最近使用的对象用强引用存储在LinkedHashMap中,当缓存满时,把最近最少使用的对象从内存中移除,并提供了get和put方法来完成缓存的获取和添加操作。
LruCache的使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
int cacheSize = (int) (Runtime.getRuntime().totalMemory() / 8);
LruCache<String, Bitmap> mMemoryCache = new LruCache<String, Bitmap>(cacheSize) {
@Override
protected int sizeOf(String key, Bitmap value) {
return value.getByteCount();
}
};
|
NOTE:缓存的总容量和每个缓存对象的大小所用的单位要一致。
LruCache的实现原理
LruCache的核心思想:维护一个缓存对象列表,其中对象列表的排列方式是按照访问顺序实现的,即一直没有访问的对象,将放在队头,最早被淘汰,而最近访问的对象将放在队尾,最晚被淘汰。
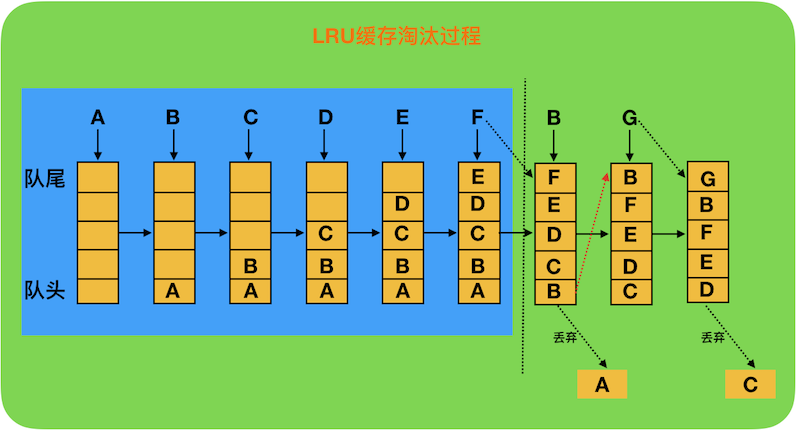
LruCache的实现是使用LinkedHashMap来维护这个对象队列的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
|
LinkedHashMap使用示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
LinkedHashMap<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(0, 0.75f, true);
map.put("A", "A");
map.put("B", "B");
map.put("C", "C");
map.put("D", "D");
map.put("E", "E");
map.put("F", "F");
map.get("A");
map.get("B");
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
Log.i("TAG", "key:" + entry.getKey() + " value:" + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
|
运行结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| I/TAG: key:C value:C
I/TAG: key:D value:D
I/TAG: key:E value:E
I/TAG: key:F value:F
I/TAG: key:A value:A
I/TAG: key:B value:B
|
LruCache的源码解析
构造方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(0, 0.75f, true);
}
|
从构造方法可以看出,使用的是LinkedHashMap的访问顺序。
put()方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public final V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
putCount++;
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);
previous = map.put(key, value);
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}
|
trimToSize()方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName() + ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
if (size <= maxSize) {
break;
}
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.eldest();
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
map.remove(key);
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
evictionCount++;
}
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}
|
get()方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| public final V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V mapValue;
synchronized (this) {
mapValue = map.get(key);
if (mapValue != null) {
hitCount++;
return mapValue;
}
missCount++;
}
V createdValue = create(key);
if (createdValue == null) {
return null;
}
synchronized (this) {
createCount++;
mapValue = map.put(key, createdValue);
if (mapValue != null) {
map.put(key, mapValue);
} else {
size += safeSizeOf(key, createdValue);
}
}
if (mapValue != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, createdValue, mapValue);
return mapValue;
} else {
trimToSize(maxSize);
return createdValue;
}
}
|
LinkedHashMap的get()方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
|
afterNodeAccess()方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) {
LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}
|
参考链接
- 彻底解析Android缓存机制——LruCache
- LruCache 源码解析
- Android源码解析——LruCache
