概述
SharedPreferences(简称SP)是Android中常用的数据存储方式,SP采用key-value(键值对)形式,主要用于轻量级的数据存储,尤其适合保存应用的配置参数,但不建议使用SP来存储大规模的数据,可能会降低性能。
SP采用XML文件格式来保存数据,该文件位于/data/data/<packageName>/shared_prefs/。
使用示例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 SharedPreferences sp = getSharedPreferences("my_prefs" , Context.MODE_PRIVATE); SharedPreferences.Editor editor = sp.edit(); editor.putString("blog" , "www.xucanhui.com" ); boolean result = editor.commit(); String blog = sp.getString("blog" , "" );
my_prefs.xml文件内容:
1 2 3 4 <?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8' standalone='yes' ?> <map > <string name ="blog" > www.xucanhui.com</string > </map >
架构
来源:http://gityuan.com/2017/06/18/SharedPreferences/
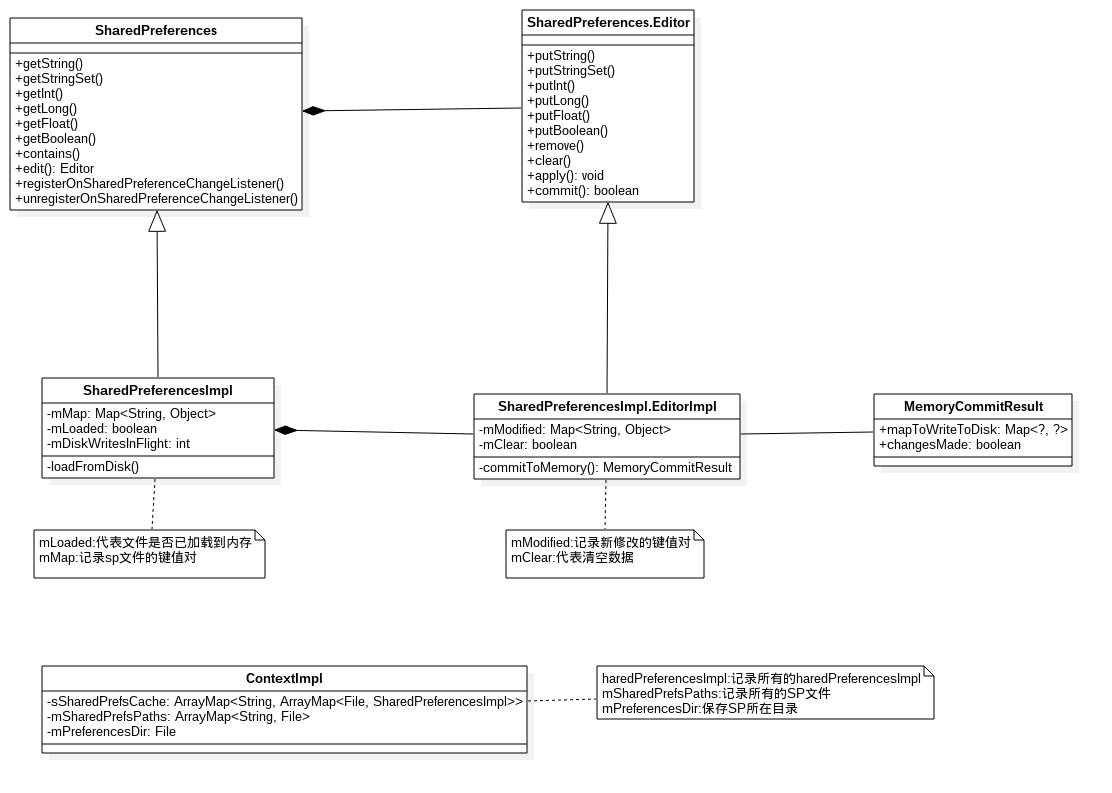
类图
说明 :SharedPreferences与Editor只是两个接口,SharedPreferencesImpl和EditorImp分别实现了对应的接口。另外,ContextImpl记录着SharedPreferences的重要数据,如下:
sSharedPrefsCache:以包名为key,二级key是SP文件,以SharedPreferencesImp为value的嵌套map结构,sSharedPrefsCache是静态成员变量,每个进程只有唯一的一份,且由ContextImpl.class锁保护。
mSharedPrefsPaths:记录所有的SP文件,以文件名为key,具体文件为value的map结构。
mPreferencesDir:是值SP所在目录,即/data/data/<packageName>/shared_prefs/
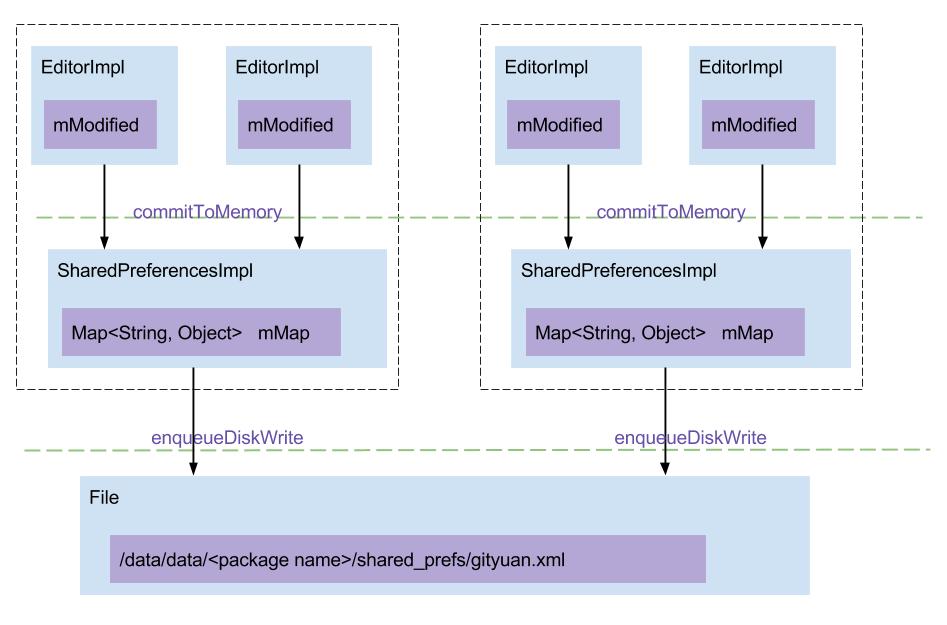
工作流程
说明 :
putXxx()操作:把数据写入到EditorImpl.mModified;
apply()或者commit()操作:
a. 先调用commitToMemory(),将数据同步到SharedPreferencesImpl的mMap,并保存到MemoryCommitResult的mapToWriteToDisk;
b. 再调用enqueueDiskWrite(),写入到磁盘文件;在这之前把原有数据保存到.bak后缀的文件,用于在写磁盘的过程出现任何异常可恢复数据。
getXxx()操作:从SharedPreferencesImpl.mMap读取数据。
源码分析(API 28) 获取SharedPreferences
可以通过Activity.getPreferences(mode)、PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(context)或者Context.getSharedPreferences(name,mode)来获取SharedPreferences实例,
最终调用的是ContextImpl的getSharedPreferences(name, mode)。
ContextImpl#getSharedPreferences(name, mode) :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class ContextImpl extends Context @GuardedBy ("ContextImpl.class" ) private ArrayMap<String, File> mSharedPrefsPaths; @Override public SharedPreferences getSharedPreferences (String name, int mode) File file; synchronized (ContextImpl.class) { if (mSharedPrefsPaths == null ) { mSharedPrefsPaths = new ArrayMap<>(); } file = mSharedPrefsPaths.get(name); if (file == null ) { file = getSharedPreferencesPath(name); mSharedPrefsPaths.put(name, file); } } return getSharedPreferences(file, mode); } @Override public File getSharedPreferencesPath (String name) return makeFilename(getPreferencesDir(), name + ".xml" ); } private File getPreferencesDir () synchronized (mSync) { if (mPreferencesDir == null ) { mPreferencesDir = new File(getDataDir(), "shared_prefs" ); } return ensurePrivateDirExists(mPreferencesDir); } } }
ContextImpl#getSharedPreferences(file, mode) :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 @Override public SharedPreferences getSharedPreferences (File file, int mode) SharedPreferencesImpl sp; synchronized (ContextImpl.class) { final ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl> cache = getSharedPreferencesCacheLocked(); sp = cache.get(file); if (sp == null ) { checkMode(mode); if (getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.O) { if (isCredentialProtectedStorage() && !getSystemService(UserManager.class) .isUserUnlockingOrUnlocked(UserHandle.myUserId())) { throw new IllegalStateException("SharedPreferences in credential encrypted " + "storage are not available until after user is unlocked" ); } } sp = new SharedPreferencesImpl(file, mode); cache.put(file, sp); return sp; } } if ((mode & Context.MODE_MULTI_PROCESS) != 0 || getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion < android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB) { sp.startReloadIfChangedUnexpectedly(); } return sp; } @GuardedBy ("ContextImpl.class" )private ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl> getSharedPreferencesCacheLocked () if (sSharedPrefsCache == null ) { sSharedPrefsCache = new ArrayMap<>(); } final String packageName = getPackageName(); ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl> packagePrefs = sSharedPrefsCache.get(packageName); if (packagePrefs == null ) { packagePrefs = new ArrayMap<>(); sSharedPrefsCache.put(packageName, packagePrefs); } return packagePrefs; }
SharedPreferencesImpl初始化 :
SharedPreferencesImpl.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 SharedPreferencesImpl(File file, int mode) { mFile = file; mBackupFile = makeBackupFile(file); mMode = mode; mLoaded = false ; mMap = null ; mThrowable = null ; startLoadFromDisk(); }
SharedPreferencesImpl#startLoadFromDisk() :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 private void startLoadFromDisk () synchronized (mLock) { mLoaded = false ; } new Thread("SharedPreferencesImpl-load" ) { public void run () loadFromDisk(); } }.start(); } private void loadFromDisk () synchronized (mLock) { if (mLoaded) { return ; } if (mBackupFile.exists()) { mFile.delete(); mBackupFile.renameTo(mFile); } } if (mFile.exists() && !mFile.canRead()) { Log.w(TAG, "Attempt to read preferences file " + mFile + " without permission" ); } Map<String, Object> map = null ; StructStat stat = null ; Throwable thrown = null ; try { stat = Os.stat(mFile.getPath()); if (mFile.canRead()) { BufferedInputStream str = null ; try { str = new BufferedInputStream( new FileInputStream(mFile), 16 * 1024 ); map = (Map<String, Object>) XmlUtils.readMapXml(str); } catch (Exception e) { Log.w(TAG, "Cannot read " + mFile.getAbsolutePath(), e); } finally { IoUtils.closeQuietly(str); } } } catch (ErrnoException e) { } catch (Throwable t) { thrown = t; } synchronized (mLock) { mLoaded = true ; mThrowable = thrown; try { if (thrown == null ) { if (map != null ) { mMap = map; mStatTimestamp = stat.st_mtim; mStatSize = stat.st_size; } else { mMap = new HashMap<>(); } } } catch (Throwable t) { mThrowable = t; } finally { mLock.notifyAll(); } } }
获取SharedPreferences总结 :
首次使用则创建相应xml文件;
异步加载文件内容到内存,此时执行getXxx()和edit()方法都是阻塞等待的,直到文件数据全部加载到内存;
一旦数据完全加载到内存,后续的getXxx()则是直接访问内存。
获取数据 SharedPreferencesImpl#getString(key, defValue) :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public String getString (String key, @Nullable String defValue) synchronized (mLock) { awaitLoadedLocked(); String v = (String)mMap.get(key); return v != null ? v : defValue; } } private void awaitLoadedLocked () if (!mLoaded) { BlockGuard.getThreadPolicy().onReadFromDisk(); } while (!mLoaded) { try { mLock.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException unused) { } } if (mThrowable != null ) { throw new IllegalStateException(mThrowable); } }
编辑数据 获取Editor编辑器实例:SharedPreferencesImpl#edit()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public Editor edit () synchronized (mLock) { awaitLoadedLocked(); } return new EditorImpl(); }
EditorImpl#putString(key, value) :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public final class EditorImpl implements Editor @GuardedBy ("mEditorLock" ) private final Map<String, Object> mModified = new HashMap<>(); @GuardedBy ("mEditorLock" ) private boolean mClear = false ; public Editor putString (String key, @Nullable String value) synchronized (mEditorLock) { mModified.put(key, value); return this ; } } public Editor remove (String key) synchronized (mEditorLock) { mModified.put(key, this ); return this ; } } public Editor clear () synchronized (mEditorLock) { mClear = true ; return this ; } } }
保存数据
保存数据,主要是调用commit()和apply()方法来完成的。
EditorImpl#commit()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public boolean commit () MemoryCommitResult mcr = commitToMemory(); SharedPreferencesImpl.this .enqueueDiskWrite( mcr, null ); try { mcr.writtenToDiskLatch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { return false ; } notifyListeners(mcr); return mcr.writeToDiskResult; }
EditorImpl#commitToMemory()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 private MemoryCommitResult commitToMemory () long memoryStateGeneration; List<String> keysModified = null ; Set<OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener> listeners = null ; Map<String, Object> mapToWriteToDisk; synchronized (SharedPreferencesImpl.this .mLock) { if (mDiskWritesInFlight > 0 ) { mMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(mMap); } mapToWriteToDisk = mMap; mDiskWritesInFlight++; boolean hasListeners = mListeners.size() > 0 ; if (hasListeners) { keysModified = new ArrayList<String>(); listeners = new HashSet<OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener>(mListeners.keySet()); } synchronized (mEditorLock) { boolean changesMade = false ; if (mClear) { if (!mapToWriteToDisk.isEmpty()) { changesMade = true ; mapToWriteToDisk.clear(); } mClear = false ; } for (Map.Entry<String, Object> e : mModified.entrySet()) { String k = e.getKey(); Object v = e.getValue(); if (v == this || v == null ) { if (!mapToWriteToDisk.containsKey(k)) { continue ; } mapToWriteToDisk.remove(k); } else { if (mapToWriteToDisk.containsKey(k)) { Object existingValue = mapToWriteToDisk.get(k); if (existingValue != null && existingValue.equals(v)) { continue ; } } mapToWriteToDisk.put(k, v); } changesMade = true ; if (hasListeners) { keysModified.add(k); } } mModified.clear(); if (changesMade) { mCurrentMemoryStateGeneration++; } memoryStateGeneration = mCurrentMemoryStateGeneration; } } return new MemoryCommitResult(memoryStateGeneration, keysModified, listeners, mapToWriteToDisk); }
EditorImpl#enqueueDiskWrite()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 private void enqueueDiskWrite (final MemoryCommitResult mcr, final Runnable postWriteRunnable) final boolean isFromSyncCommit = (postWriteRunnable == null ); final Runnable writeToDiskRunnable = new Runnable() { @Override public void run () synchronized (mWritingToDiskLock) { writeToFile(mcr, isFromSyncCommit); } synchronized (mLock) { mDiskWritesInFlight--; } if (postWriteRunnable != null ) { postWriteRunnable.run(); } } }; if (isFromSyncCommit) { boolean wasEmpty = false ; synchronized (mLock) { wasEmpty = mDiskWritesInFlight == 1 ; } if (wasEmpty) { writeToDiskRunnable.run(); return ; } } QueuedWork.queue(writeToDiskRunnable, !isFromSyncCommit); }
EditorImpl#writeToFile()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 private void writeToFile (MemoryCommitResult mcr, boolean isFromSyncCommit) boolean fileExists = mFile.exists(); if (fileExists) { boolean needsWrite = false ; if (mDiskStateGeneration < mcr.memoryStateGeneration) { if (isFromSyncCommit) { needsWrite = true ; } else { synchronized (mLock) { if (mCurrentMemoryStateGeneration == mcr.memoryStateGeneration) { needsWrite = true ; } } } } if (!needsWrite) { mcr.setDiskWriteResult(false , true ); return ; } boolean backupFileExists = mBackupFile.exists(); if (!backupFileExists) { if (!mFile.renameTo(mBackupFile)) { Log.e(TAG, "Couldn't rename file " + mFile + " to backup file " + mBackupFile); mcr.setDiskWriteResult(false , false ); return ; } } else { mFile.delete(); } } try { FileOutputStream str = createFileOutputStream(mFile); if (str == null ) { mcr.setDiskWriteResult(false , false ); return ; } XmlUtils.writeMapXml(mcr.mapToWriteToDisk, str); writeTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); FileUtils.sync(str); fsyncTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); str.close(); ContextImpl.setFilePermissionsFromMode(mFile.getPath(), mMode, 0 ); try { final StructStat stat = Os.stat(mFile.getPath()); synchronized (mLock) { mStatTimestamp = stat.st_mtim; mStatSize = stat.st_size; } } catch (ErrnoException e) { } if (DEBUG) { fstatTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); } mBackupFile.delete(); mDiskStateGeneration = mcr.memoryStateGeneration; mcr.setDiskWriteResult(true , true ); return ; } catch (XmlPullParserException e) { Log.w(TAG, "writeToFile: Got exception:" , e); } catch (IOException e) { Log.w(TAG, "writeToFile: Got exception:" , e); } if (mFile.exists()) { if (!mFile.delete()) { Log.e(TAG, "Couldn't clean up partially-written file " + mFile); } } mcr.setDiskWriteResult(false , false ); }
EditorImpl#apply()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public void apply () final long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); final MemoryCommitResult mcr = commitToMemory(); final Runnable awaitCommit = new Runnable() { @Override public void run () try { mcr.writtenToDiskLatch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException ignored) { } } }; QueuedWork.addFinisher(awaitCommit); Runnable postWriteRunnable = new Runnable() { @Override public void run () awaitCommit.run(); QueuedWork.removeFinisher(awaitCommit); } }; SharedPreferencesImpl.this .enqueueDiskWrite(mcr, postWriteRunnable); notifyListeners(mcr); }
性能优化 IO瓶颈
IO瓶颈是造成SP性能差的最大原因,解决IO瓶颈,80%的性能问题就解决了。
SP的IO瓶颈包括读取数据到内存与数据写入磁盘两部分。
读取数据到内存有两个场景会触发:
a. SP文件没有被加载到内存时,调用getSharedPreferences方法会初始化文件并读入内存。
b. 版本低于Android-H或使用了MULTI_PROCESS标记时,每次调用getSharedPreference方法时都会读入。
优化 :
我们可以优化的便是b了,每次加载数据到内存太过影响效率,但H以下版本已经很低了,基本可以忽略。
对于MULTI_PROCESS,可以采用ContentProvider等其他方式,效率更好,而且可避免SP数据丢失的情况。
数据写入到磁盘也有两个场景会触发:
a. Editor的commit方法,每次执行时同步写入磁盘。
b. Editor的apply方法,每次执行时在单线程池中写入磁盘,异步写入。
优化 :
commit和apply的方法区别在于同步写入和异步写入,以及是否需要返回值。
在不需要返回值的情况下,使用apply方法可以极大的提高性能。
同时,多个写入操作可以合并为一个commit/apply,将多个写入操作合并后也能提高IO性能。
锁性能差
SP的get操作,会锁定SharedPreferences对象,互斥其他操作。
SP的put操作,edit()及commitToMemory会锁定SharedPreferences对象,put操作会锁定Editor对象,写入磁盘更会锁定一个写入锁。
优化 :
由于锁的缘故,SP操作并发时,耗时会增加。减少锁耗时,是一个优化点。
由于读写操作的锁均是SP实例对象的,将数据分拆到不同的sp文件中,便是减少锁耗时的直接方案。
降低单文件访问频率,多文件均摊访问,以减少锁耗时。
优化总结
强烈建议不要在sp里面存储特别大的key/value, 有助于减少卡顿/anr;
请不要高频地使用apply, 尽可能地批量提交;commit直接在主线程操作, 更要注意了;
不要使用MODE_MULTI_PROCESS;
高频写操作的key与高频读操作的key可以适当地拆分文件, 由于减少同步锁竞争;
不要一上来就执行getSharedPreferences().edit(), 应该分成两大步骤来做, 中间可以执行其他代码;
不要连续多次edit(), 应该获取一次获取edit(),然后多次执行putxxx(), 减少内存波动; 经常看到大家喜欢封装方法, 结果就导致这种情况的出现;
每次commit时会把全部的数据更新的文件, 所以整个文件是不应该过大的, 影响整体性能。
参考链接
SharedPreferences 全面剖析SharedPreferences SharedPreferences优化总结 Best Practice - SharedPreferences Pros and Cons of SQLite and Shared Preferences 庖丁解牛之SharedPreferences超级大卡顿